Lesson 5 – Constructive Alignment
Which of the following assessments can best showcase that this learning outcome has been achieved (select all that apply):
“Analyze the differences between working in unionized and non-unionized workplaces.”
- Case study
- Infographic
- Discussion board post
- Quiz (true and false questions)
- Oral presentation
- Essay
Click here for the correct answer
Correct answer: All except D.
The learning outcome focuses on analysis, which requires students to break down information in order to examine relationships. Using the ICE model here, students are expected to showcase learning at the connections stage, drawing both from personal experiences related to the topic and by drawing out both common and unique aspects of unionized and non-unionized work environments. While this level of thinking is not as easily demonstrated through a quiz format, students can show evidence of learning through all other assessment types, which prompt deeper reasoning and meaning-making.
Now, reflect on your assessment. Can the learning outcome for your assessment be achieved through more than one type of assessment? If yes, think about ways to provide options and flexibility for students as they demonstrate their learning. If no, why might this be the case?
When learning outcomes, assessments, and activities are aligned, students can focus on learning. The lesson (or module) activities support students in achieving the course learning outcomes as measured by the assessments, which in turn contribute to achieving the course, and ultimately, the program learning outcomes.
In other words, the activities build or scaffold toward the development of the knowledge, skills, and attitudes described by the outcomes and measured by the assessments. Clear connections between learning outcomes and assignments help students see the purpose of assignments, understand instructor explanations, and follow a logical path for learning. This approach also helps ensure that the course is aligned with the program outcomes mapping and accreditation standards. Alignment contributes to the quality of instruction, contributes to student sense of belonging and motivation, and ensures that courses fulfil industry and ministry requirements.
The diagram below illustrates the constructive alignment approach, as described by Biggs (1996). The diagram visually represents the alignment of these three elements as essential components of effective educational design that can support student motivation and belonging.
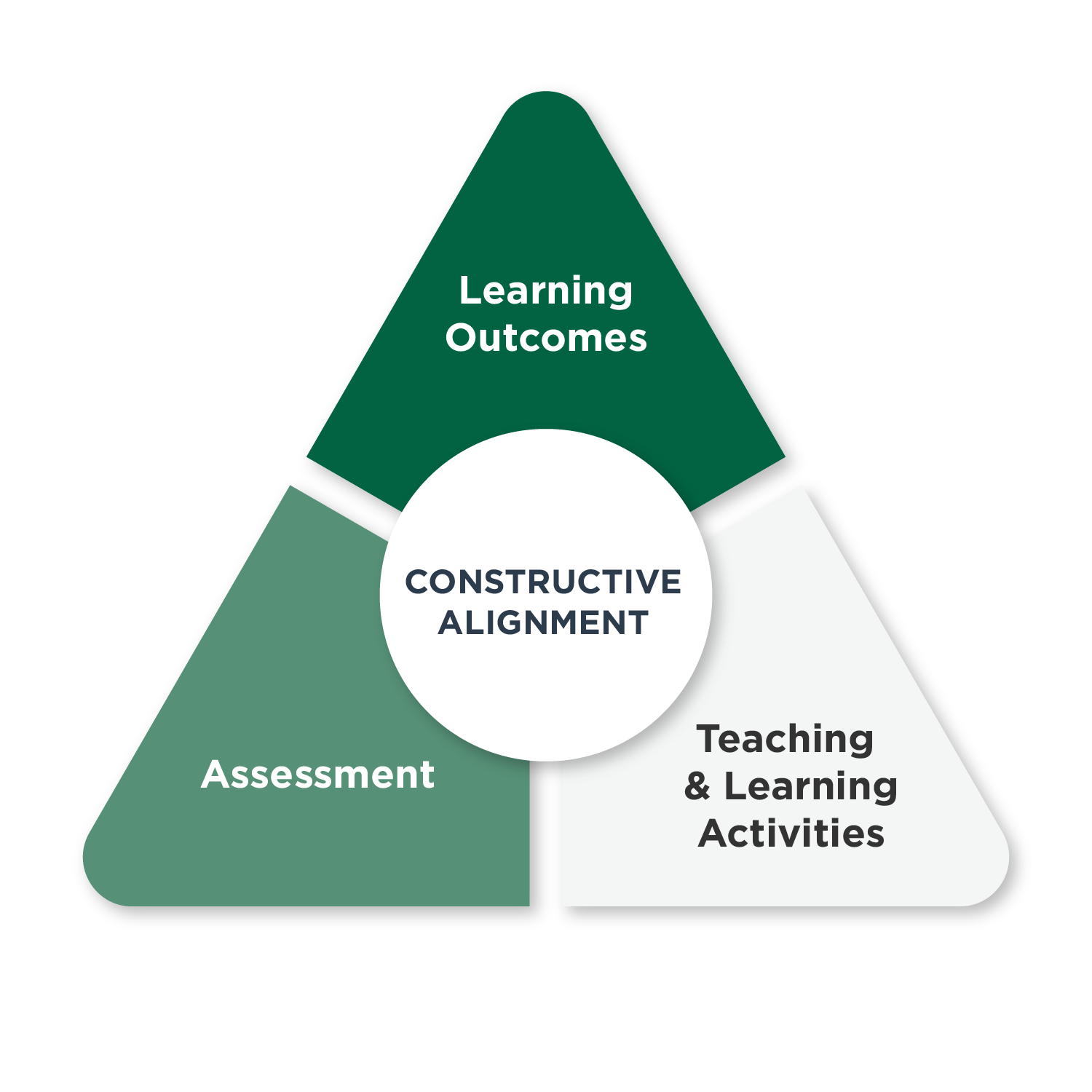
Learning Outcomes: Articulate what you want your students to learn and how it will be demonstrated.
Assessment: Clearly define how students will be graded (grading rubrics).
Activities: Make it easy for students to engage and feel empowered.