Flipped Learning
What is the Flipped Classroom?
Flipping the classroom is a blended learning approach that places the lecture (or core learning content) outside of class time so that the teacher can spend more time in class interacting and working with students. Refer to this article from Vanderbilt University.
How Does it Work?
“Flipped learning is an approach where students gain necessary knowledge before class, and instructors guide students to actively and interactively clarify and apply that knowledge during class.” Refer to this article from the University of Texas.
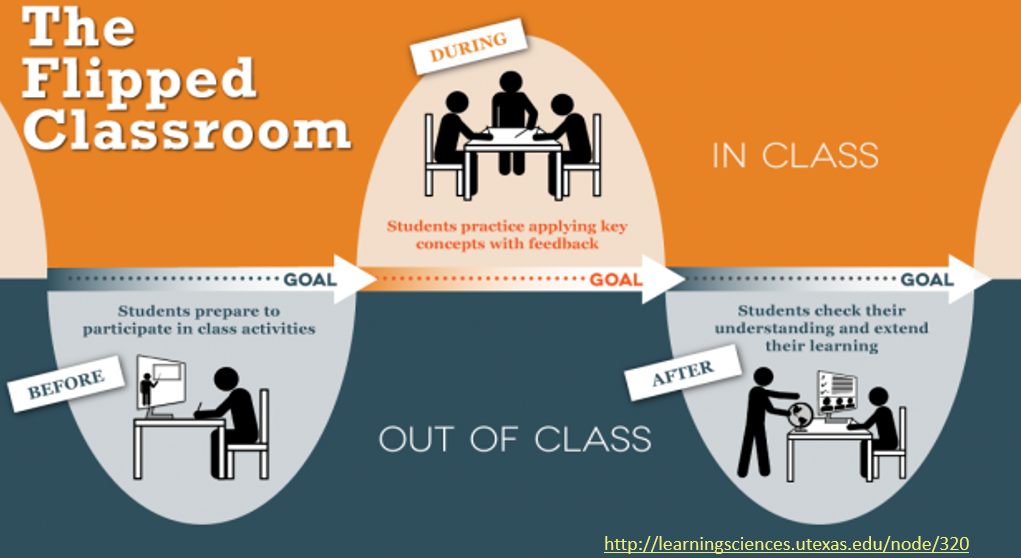
Retrieved on 02/29/2016 from http://learningsciences.utexas.edu/teaching/flipping-a-class/how/clarify-connections
The common flipped learning practice is for lectures or core course content to be provided to students as video for self-review. However, the content can be presented in various ways such as: interactive tutorials, screencast mini-lectures (e.g. short narrated presentations), audio clips, and even traditional textbook readings and articles. Students review content out-of-class, as preparation for in-class learning activities.
| FLIPPED | TRADITIONAL |
|---|---|
| Student at Home | Student in Class |
| Teacher provides student with lesson content (video, text articles, tutorials etc.)
Student reviews lesson content on their own. |
Teacher delivers lecture
Students takes notes Student follows guided instructions Teachers assigns homework Students takes test or exam |
| Student in Class | Student at Home |
| Students work on activities to gain deeper understanding of concepts, get clarification and apply knowledge
Teacher guides, supports student activity, and provides immediate feedback |
Student completes homework
Teacher marks the homework; feedback is provide after homework completion. |
Adapted from on 08/12/2015 from: http://www.dreambox.com/blog/flipped-classroom-elementary-school-tool
What Are the Advantages?
The value of a flipped approach is that valuable class time is used to support a deeper-level of understanding through active learning activities. For example, students can work in groups to apply new knowledge or review hard-to-grasp concepts. During class, teachers coach, clarify, and advise students as they work through activities. Essentially, it is a shift of focus in which learning is less about “covering” content and more about constructing a deeper understanding through analysis, application, and problem-solving.
Key Considerations
Effective application of the flipped classroom approach requires role changes for both faculty and students. During class, the teacher functions less as the provider of content and more as learning coach and facilitator. In turn, students take ownership of their learning; instead of being passive receivers of content, they are engaged participants in activities requiring knowledge application or a deeper level of concept mastery.
Careful planning of flipped classroom activities is very important. Students should perceive a clear connection between the out-of-class content and how it is applied or reinforced in-class. Therefore, it is critical to structure out-of-class lesson content as activities with clear guiding questions that prepare students for the planned in-class application activity.
Technology and the Flipped Classroom
In the flipped classroom, technology can play a very important role.
On the one hand, “flipped” content can be interactive media such as videos or interactive tutorials. OER (Open Educational Resources) for specific concepts or topics may already exist. Or, faculty can create their own “screencast lecturettes” based on topics within their PowerPoint presentations; free authoring tools, such as MyMediaSite (https://www.algonquincollege.com/lts/mymediasite/) allow faculty to create short, reusable lessons.
Brightspace, which is currently Algonquin’s learning management system (LMS), can be especially helpful with supporting flipped learning. As a virtual extension of the classroom, a Brightspace course space can serve as central hub that connects out-of-class work with in-class work. “Flipped content” activities can be provided within the Brightspace course and student progress can be tracked. Students can complete collaborative “in-class” tasks within Brightspace by means of features such as groups and discussions. Furthermore, content reinforcement activities, such as Brightspace review quizzes, can provide pre-class review of key concepts before the in-class activity or serve as post-class reinforcement.
Pioneers of the Flipped Classroom
While versions of the flipped or “inverted classroom” has been around since the late 90’s, Jonathan Bergman and Aaron Sams are the high school teachers who popularized the approach.
Aaron Sams Discusses his Flipped Classroom Experiences
Newscast Featuring the Founders of the Flipped Classroom
Interested in Learning More?
Interested in seeing whether this approach could work for you? Learning and Teaching Services is available to help!
Contact LTS@algonquincollege.com.